In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the packaging production line plays a critical role in ensuring products are safely, efficiently, and attractively delivered to consumers. From food and beverage to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and electronics, a well-optimized packaging production line is vital for maintaining quality, reducing costs, and staying competitive in the global market.
What is a Packaging Production Line?
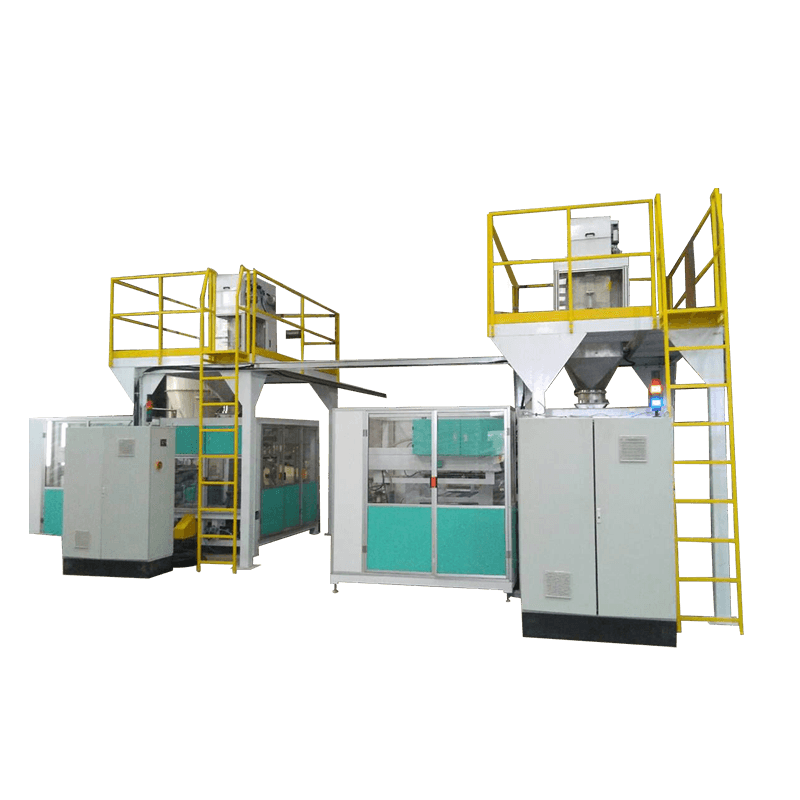
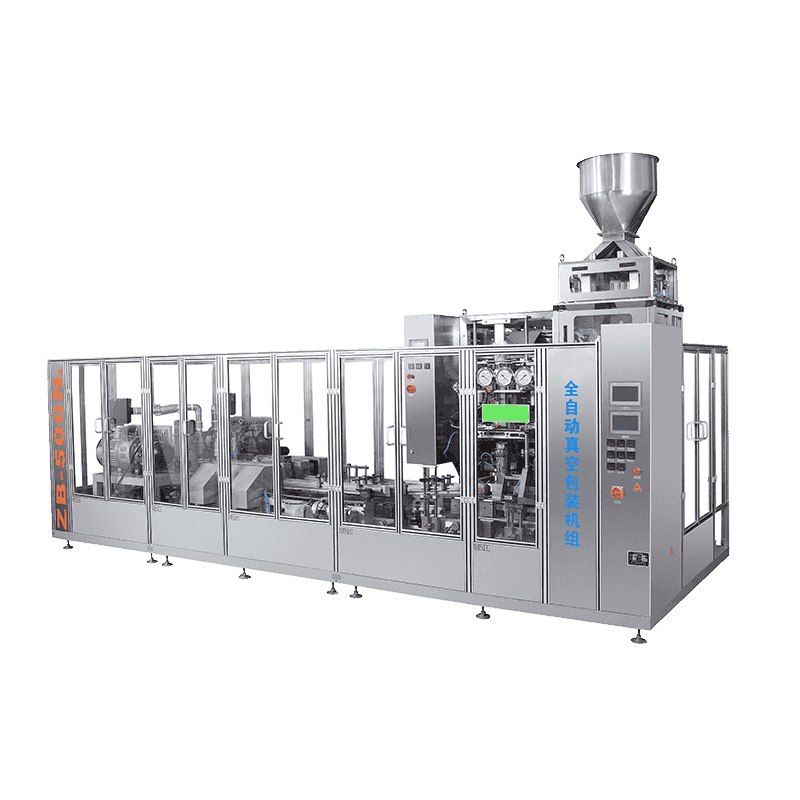
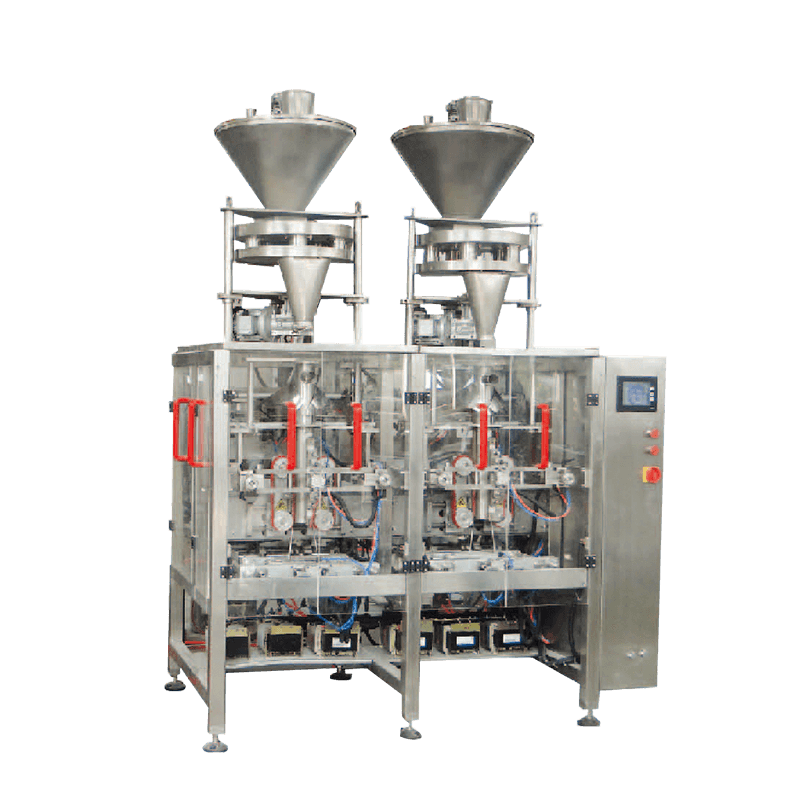
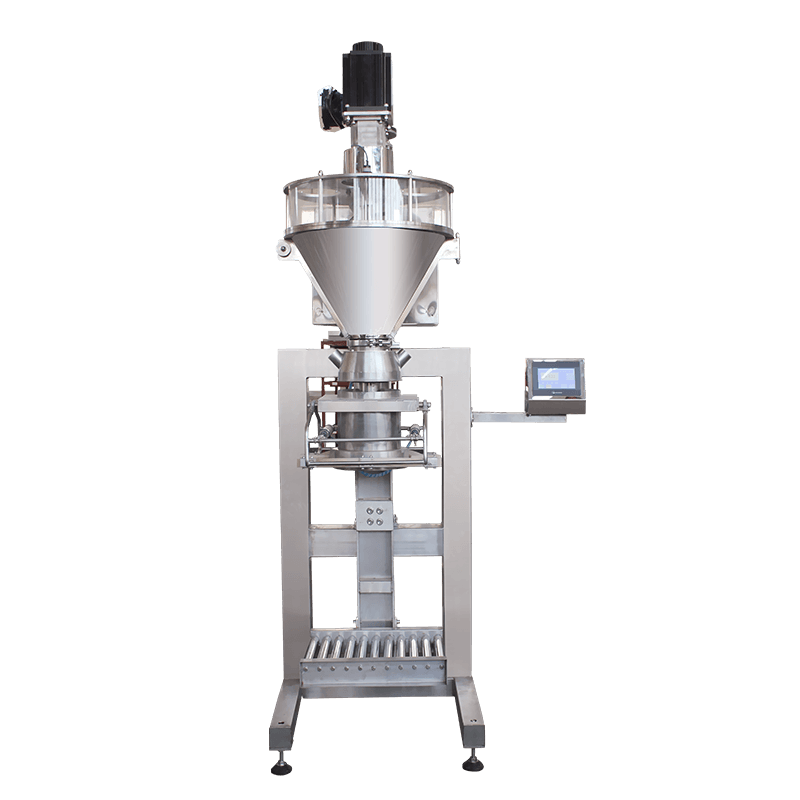
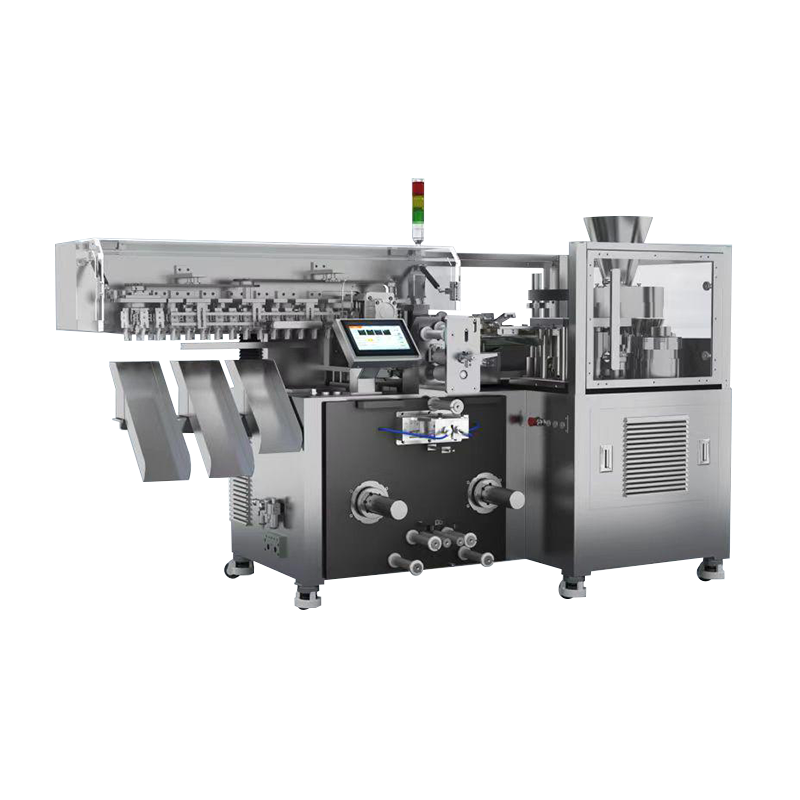
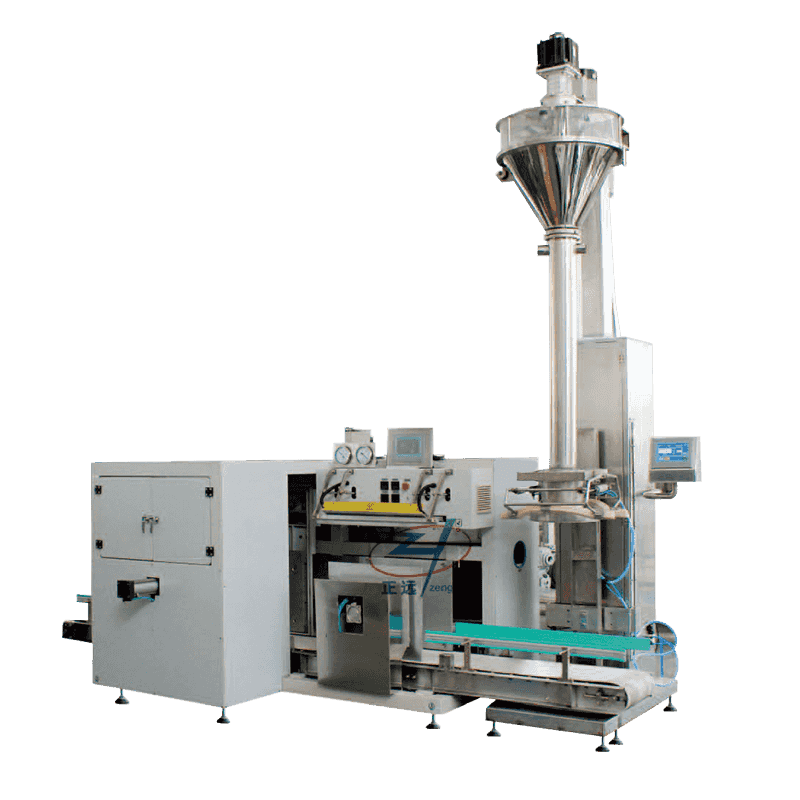
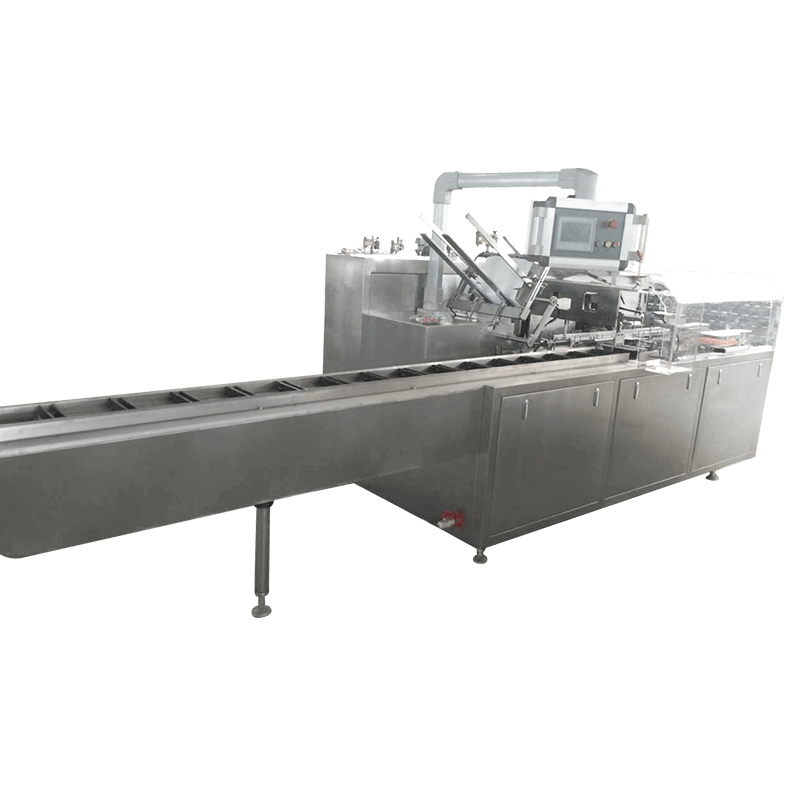
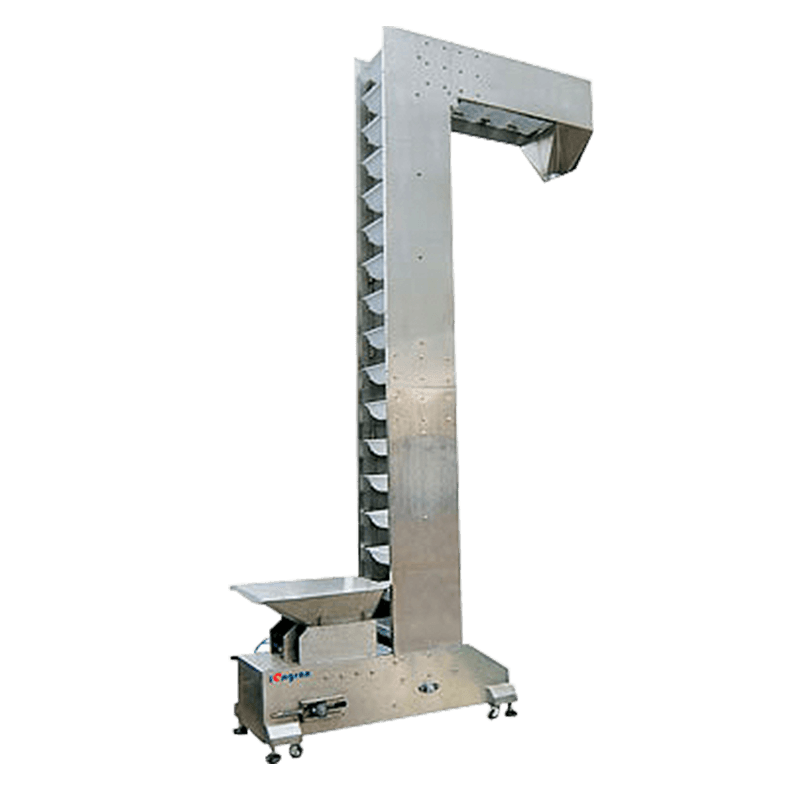
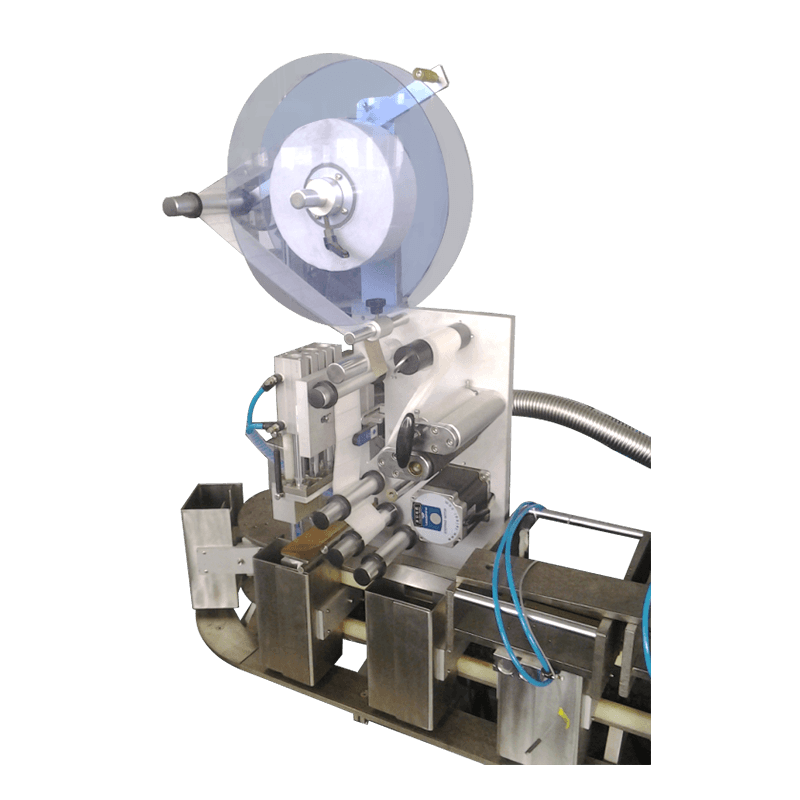
A packaging production line is an integrated system composed of multiple machines and technologies designed to perform specific packaging tasks in sequence. These tasks may include filling, sealing, labeling, coding, wrapping, palletizing, and more. Depending on the industry, the line can be fully automated, semi-automated, or manual, offering flexibility based on production volume and operational needs.
Key Components of a Packaging Line
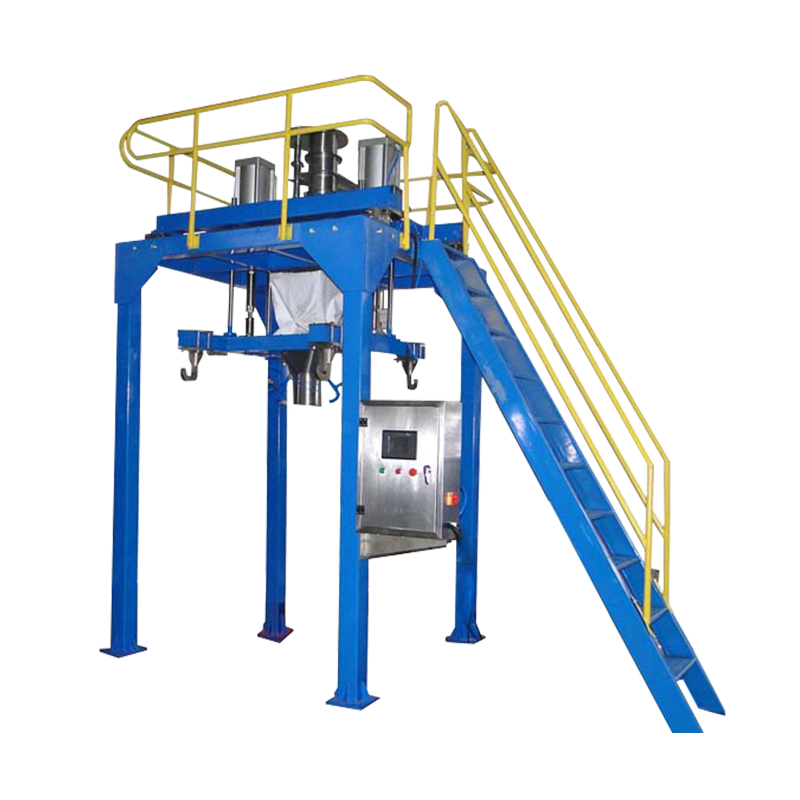
Filling Machines – These are used to fill containers, bottles, or pouches with products like liquids, powders, or solids. Precision and hygiene are crucial, especially in the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
Sealing and Capping Machines – After filling, the packaging must be securely sealed or capped to ensure freshness and prevent contamination.
Labeling and Printing Systems – Automated labelers apply product labels, while printers add batch codes, barcodes, or expiration dates for traceability and compliance.
Conveyors – These systems transport products from one station to another, enhancing speed and consistency throughout the process.
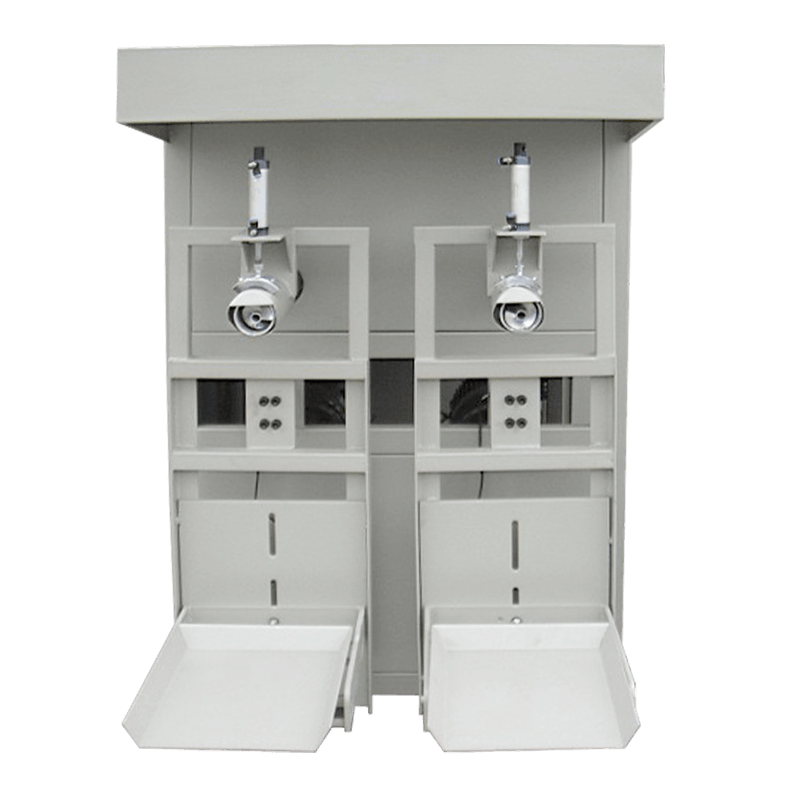
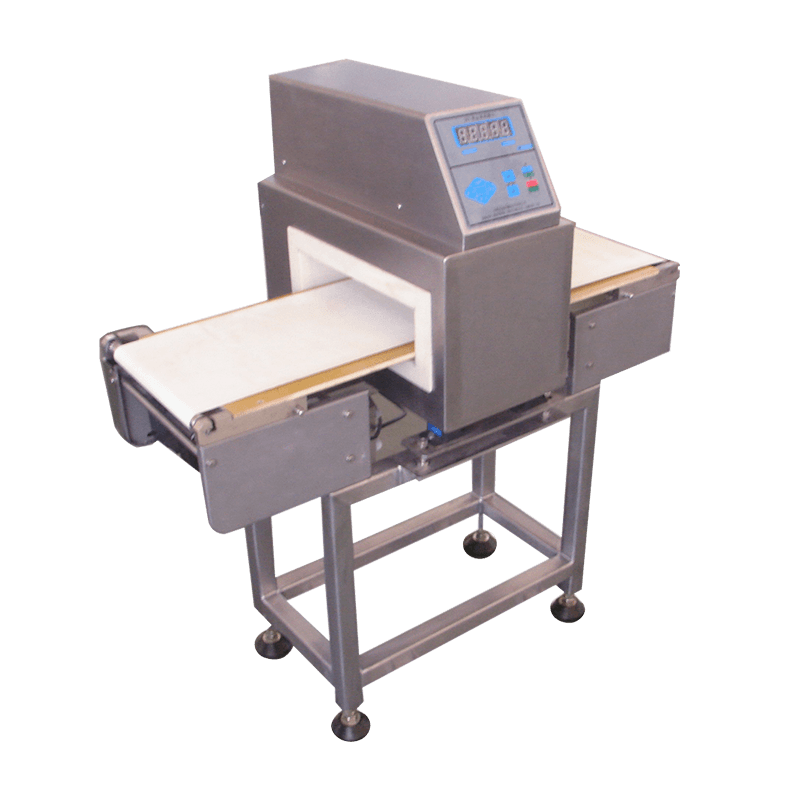
Inspection Systems – Advanced vision and weight-checking equipment help maintain quality control by detecting defects or inconsistencies.
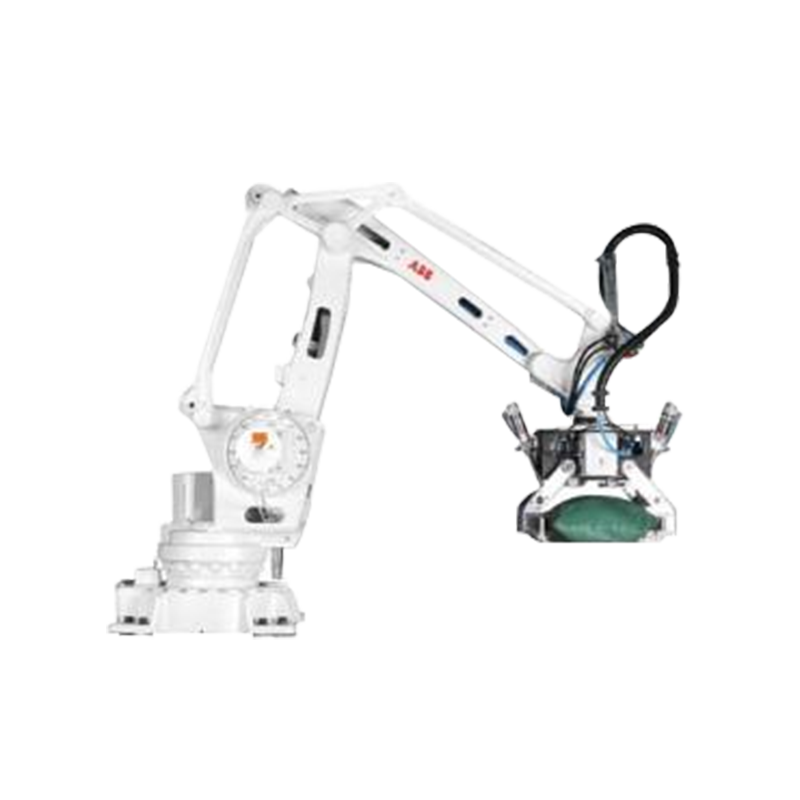
Cartoning and Palletizing – At the end of the line, products are grouped, boxed, and stacked for shipment or storage.
Benefits of an Automated Packaging Line
Increased Productivity: Automated systems can operate 24/7 with minimal downtime, significantly increasing output.
Consistent Quality: Uniform packaging reduces human error and ensures product integrity.
Cost Efficiency: Reduced labor costs, material waste, and production errors translate into substantial savings.
Scalability: Lines can be upgraded or modified to accommodate new products or changing market demands.
Data Integration: Modern lines support digital monitoring and reporting for better production management.
Customization and Industry Applications
Packaging lines can be customized to meet the unique requirements of different industries. For instance, food and beverage lines focus on hygiene and speed, while pharmaceutical packaging emphasizes precision and compliance with regulatory standards. Cosmetics packaging lines may require delicate handling and aesthetic finishes, while industrial packaging focuses on durability and bulk handling.
Future Trends in Packaging Production Lines
Smart Automation: Integration of AI and IoT technologies allows real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control of packaging processes.
Sustainability: Eco-friendly materials, minimal packaging designs, and energy-efficient machines are becoming key considerations.
Flexibility: Modular systems allow for quick changeovers between different product types or packaging formats.
Human-Machine Collaboration: Cobots (collaborative robots) are being adopted to assist human workers, improving safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
A modern packaging production line is more than just a sequence of machines—it's a critical component of a company’s operational success. By leveraging the latest in automation, technology, and design, businesses can enhance product presentation, reduce costs, and respond swiftly to market needs. As innovation continues to drive the industry forward, packaging lines will only become more intelligent, sustainable, and adaptable.



 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى









Contact Us